
At PerfectBot, we’ve spent the last 5 years developing chatbots for eCommerce. A recent technological breakthrough in the form of Large Language Models (LLMs) has given us a significant boost, and we are currently expanding our business globally in English-speaking countries.
We have successfully implemented over 50 chatbots for eCommerce in the US, Canada, the UK, Australia, and New Zealand. These implementations have covered a wide variety of businesses in both B2C and B2B sectors, including everything from toy manufacturers and beauty products to mechanical parts. This article aims to take what we’ve learned and share the do’s and don’ts of implementing GPT-powered AI chatbots in eCommerce customer service.
One common misconception is that GPT models are turnkey solutions, ready to seamlessly integrate into your eCommerce operations right out of the box. It’s essential to recognize that these models, although powerful, come with inherent limitations. One of the most significant is their tendency to “hallucinate”, or generate information that is factually incorrect.
Moreover, GPT models are vulnerable to prompt injection and other malicious techniques that allow mischievous users to manipulate your chatbot into saying things you’d rather it didn’t. We’ve recently witnessed a major electronics store implement a GPT-powered chatbot that was easily fooled into recommending purchases from competitors.
All the aforementioned challenges need to be addressed before launching a GPT-based chatbot. Furthermore, to enhance the effectiveness of your chatbot, it’s crucial to add some key features it might lack, such as human handoff management, efficient chatbot knowledge base management, and conversation analytics.
It’s important to clear up the idea that AI is a magic fix. While LLM technology such as GPT can excel in specific areas, it falls short in others. Businesses should adopt a realistic and pragmatic approach, understanding what their AI chatbot can do independently and where they should hand the conversation over to human agents. For example, answering complicated questions about specific products is usually better done by people.
Consider this example: We’ve worked with customers who abandoned their chatbot projects in the early stages. Initially, we believed the chatbots were delivering accurate responses, but to our surprise, the customers found the conversations „unimpressive.” They had high expectations, but their experience didn’t align with their hopes. Unfortunately, this impatience resulted in them missing out on the big advantages that AI could give their business.
When integrating a GPT chatbot into your eCommerce operations, it’s vital to establish realistic expectations. Consider your chatbot as a new hire, a junior customer service employee with no prior experience in your business. Its knowledge is limited to the information you provide, and it’s safer for it not to go beyond this knowledge. This practice of equipping your chatbot with specific business knowledge is known as grounding.
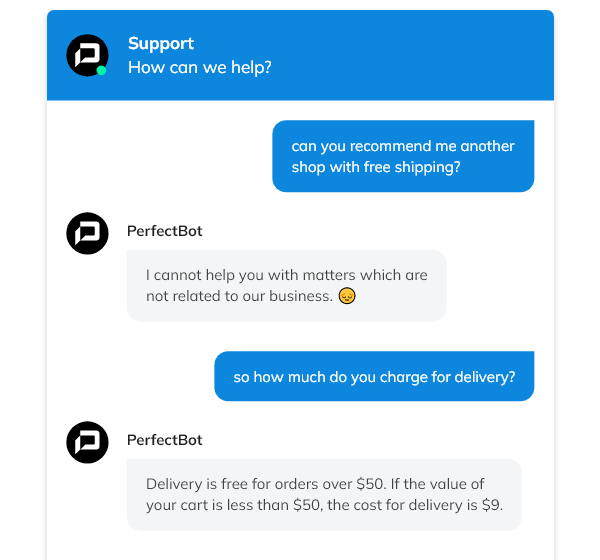
An example of a chat conversation in which the bot refuses to answer an unrelated business question.
To make sure your chatbot is well-prepared to meet the needs of your customers, you must ground it with know-how from a variety of information sources. In the eCommerce business, this covers a wide range of data, including your FAQs, help articles or tutorials, an archive of past chat or email interactions with customers (a valuable source of insights), and your business policies, especially return or shipping policies.
Additionally, you can consider incorporating training materials used by your support team. For instance, some of our customers have found success in using video content from their YouTube channels. Transcripts from these videos can serve as an excellent knowledge source for your chatbot.
By following these practices, you make sure that your chatbot is well-informed and ready to deliver relevant and accurate responses to your customers.
The first big challenge in this task is preprocessing the information from the sources we talked about earlier. These sources often contain a considerable amount of noise, which can distract the AI and increase the probability of errors in its reasoning. It’s crucial to understand that providing your chatbot with a large pile of chaotic data is not a good approach. Just as you wouldn’t do so with a new human hire, it’s essential to organize the information effectively.

An example of well-optimized copywriting for an AI chatbot.
As technology continues to evolve, it’s possible that future iterations of AI will handle such challenges better. However, you can significantly enhance the quality of AI reasoning and minimize the risk of hallucinations by providing your chatbot with a well-organized and structured knowledge base.
One of the most crucial aspects of implementing an AI chatbot in your eCommerce customer service is to establish a clear fallback policy. This policy should define specific rules for determining when the chatbot should hand over a conversation to a human agent. Here are several situations where this transition might be necessary:
Responding to explicit requests: Whenever a client explicitly requests to talk to a human agent, your chatbot should seamlessly hand over a conversation.
Detecting specific topics: Your chatbot should be able to identify topics or situations that you’ve designated for human agent service. This can include complex issues, sensitive matters, or specialized requests that require a human touch.
Detecting negative sentiment: When the chatbot detects negative sentiment or frustration in a customer’s interaction, it should be able to hand over a conversation to a human agent.
Handling unanswerable questions: In cases where the chatbot lacks the information to answer a customer’s question, it should promptly involve a human agent who can offer a satisfactory solution.
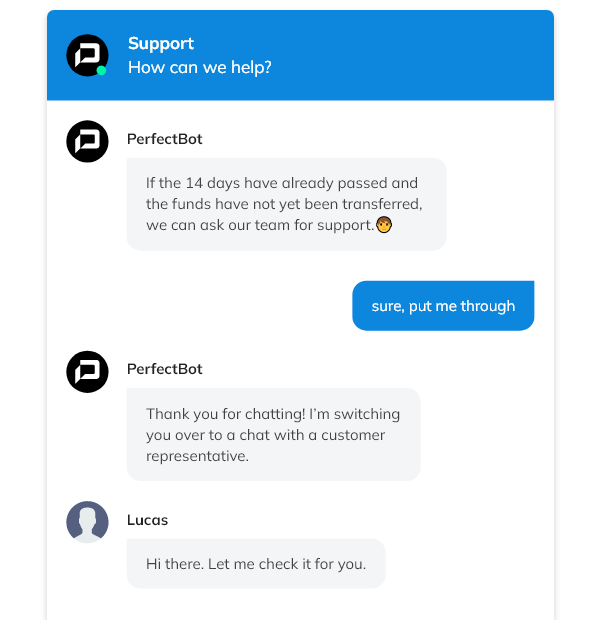
An example of a conversation in which the bot efficiently hands off to a human agent.
Another best practice is to introduce ongoing optimization into your AI chatbot strategy. To maintain top performance, you should:
Monitor conversations: Regularly oversee chatbot interactions to spot areas that need improvement.
Refine your knowledge base: Keep your chatbot’s knowledge base up-to-date by adding info, clarifying uncertainties, and ensuring accessibility.
Stay current: eCommerce data can swiftly become outdated, so make sure to refresh your knowledge base by updating the information.
This continuous optimization guarantees that your chatbot remains a valuable asset, effectively supporting your eCommerce customer service.
Case study: In several instances, we observed that chatbots which had excelled in internal tests encountered challenges when engaging with real-life customers. A simple remedy was within reach, however. With just a few days of fine-tuning and the addition of more concise information to the knowledge base, the chatbot’s proficiency in handling customer inquiries grew rapidly.
The do’s and don’ts we have mentioned are relevant to any eCommerce AI chatbot implementation. However, we recommend trying out PerfectBot.
Our GPT-powered AI chatbot is specifically designed for small and medium eCommerce sites. It can be trained on your FAQ page and other helpdesk materials to provide accurate answers to your customer questions.
Check out our website to see reviews from satisfied users, book a demo, or give it a try for free for 30 days – no strings attached.

Gorgias offers a wide variety of useful functions. It’s designed to connect all your customer service channels and manage them from one dashboard. However, one function that Gorgias doesn’t provide natively is a chatbot. Continue reading to learn just how simple it is to install one into Gorgias.
Read more
PerfectBot efficiently processes Help Center information, delivering trustworthy answers to your customers. Discover AI support optimization techniques for new or existing support materials.
Read more
Chatbot tailored for
ecommerce
Maximum Accuracy
Ready
in 1 day